Guidelines for Volunteering Programs
This guide seeks to promote volunteering programs with a strategic approach in order to achieve transformation through the empowerment of employees, so that they may take on leadership roles and become agents of change.
- Definitions
Corporate Volunteering is a practice by which a company promotes, facilitates and supports the volunteer work of its employees in order to contribute to the development and well-being of society. It must integrate at least three actors: the company, employees and community. It has the following characteristics:
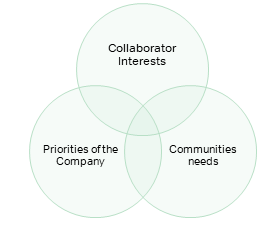
- Strategic: integrates the priorities of the company, the interests of employees and the needs of the community and is aligned with Orbia’s Social Responsibility Strategy.
- Innovative: seeks to design and execute new actions to achieve better results.
- High impact: secures outstanding results for the company, employees and community.
- Sustainable: ensures the long-term commitment of the company, employees and community.
- Replicable: projects are designed to run based on different scenarios, with efficient costs, so that their scaling is feasible.
- Transformative: offers significant life experiences for the volunteers.
2.Types of Volunteering
Below are the four types of volunteering programs in which Orbia collaborators can contribute. Participation is possible in any of the four types, according to the strategy that the local operation has chosen to manage its relationship with neighboring communities. It is also possible to implement more than one type of volunteering.
It is expected that progress is made from volunteer philanthropic actions to social investment projects, where the level of commitment of the three parties involved and the level of management needed will be greater. Projects based on skills and social investment projects should be oriented to the themes that have a closer relationship with our business.
1.Philanthropic Actions: intervention is done as humanitarian or social assistance to a vulnerable group or people. These actions must be done in neighboring communities or in regions where we have operations. They are not sustainable philanthropic activities.
Examples:
Donations and Campaigns
- Winter activities: delivering blankets, sweaters, collection and delivery of Christmas gifts to children, etc.
- Disaster response: support given to victims of disasters through collection and delivery of food, clothing, etc.
- Fundraising: collections for a specific social cause.
Role of the Employee
- Leader: guides and coordinates the work of volunteers
- Donor: contributes in cash or in kind.
- Participant: participates in raising money, collecting donations, and delivering them to the community.
Benefits
- Sensitizing employees and volunteers about the program.
- They allow significant volunteer activities, with a high level of participation within the company.
Purpose
- Generates commitment among collaborators.
- Develops a relationship with the communities
2.Activities during Events: one-day event where volunteers give their time to carry out activities for the community. Once again, these activities must be done for neighboring communities or in regions where we have operations.
Examples:
Infrastructure Events: aimed at the construction or improvement of infrastructure. Examples: construction of prefabricated houses, paint schools, conditioning of physical spaces, installation of playgrounds, etc.
- Environmental Events: focused on improving the environment, with activities such as tree planting or cleaning beaches and parks.
- Sporting Events with a Social Purpose: +Km Program.
- Educational Workshops: seeks to strengthen the capacities of beneficiaries through the transfer of knowledge from employees. The topics are chosen according to the Proposal of Value for the company, volunteers and the community. Example: Workshop "Hydros"
Role of the Employee
- Leader: guides and coordinates the work of volunteers
- Participant: contribute their work and effort
Benefits
- Volunteers and leaders are identified and is an excellent platform to strengthen institutional values prioritized by HR as communication, integration and/or teamwork.
- They allow for significant volunteer activities, with a good level of participation within the company
Purpose
- Engaging the community
- Secures internal support from Managers
- Sensitizes volunteers about the needs of the communities, engage them and motivate their participation.
- Initiatives based on skills: initiatives based on the talent and skills of the volunteers to support a community. They should preferably be oriented to water and education, which are the strategic lines defined by Orbia. They usually last from weeks to months.
Examples:
- Transfer of technical skills: provide specialized training workshops for beneficiaries like courses on piping installation and management of technological tools. It is also important to support the development of young talent in our communities, in order to have qualified people who can offer products or services to Orbia, or that can be hired in the future as employees.
- Workshops: lead or participate in educational initiatives that allow a better understanding in our communities of the challenges to achieve sustainability on issues such as climate change adaptation, disaster risk reduction, biodiversity, poverty reduction and product responsibility. Other possible topics of interest for the community are entrepreneurship workshops, business formalization conferences, artistic workshops, education and tutoring, etc.
Role of the Employee
- Leader: guides the design of the initiative
- Participant: commands the workshops established in the project.
Benefits
- Opportunity to identify skills and talent of employees outside the workplace.
- Increased impact to the community, volunteers and company.
- Attraction and talent retention
Purpose
- Encourages the volunteers to use their talent in benefit of the community and propose new ideas.
- Generates the level of commitment required in the volunteers to finish the project successfully.
- Social Investment Projects: Collaborators identify a social problem, design an intervention, and invite other volunteers to run it. They become leaders of their own projects. All Social Investment Projects have to be oriented to water and/or education, which are the strategic lines defined by Orbia. They usually need a year or more to be implemented and have a high potential to participate in the Kaluz Award. Although its application is not mandatory, it is recommended that volunteer programs that are already in this category apply.
Example:
- Social Innovation Competition: volunteers design their own social projects and present them to the Site Managers and HR Leaders. They take into account that the project needs to have a clear involvement of Orbia’s business, government and the neighboring communities.
- Some ideas are providing solutions for water piping, storage and re-use of rainwater and wastewater.
- Projects that consider Kaluz Award requirements are good examples.
Role of the Employee
- Leader: chooses a community, identifies a social problem and proposes a solution. Runs the project and mobilizes other volunteers.
- Participant: join the activities designed and proposed by the team leader.
Benefits
- Generates good long-term relationships with the community and government.
- Increases the reputation of the company.
- Promotion of social innovation.
- Generation of a high level of pride and commitment of our employees.
- Development of employee’s skills and teamwork abilities.
- Attraction and talent retention.
Purpose
- Improves the life conditions of neighboring communities and the relationship with governments through projects aligned with Orbia’s business
- Involves the three actors (community, government and volunteers) in order to have high impact benefits to all.
Note:
The responsible teams for this program are the local HR teams. Projects and initiatives have to be approved by local Managers and will be supported by the Corporate Social Responsibility Manager.
Each operation will communicate to volunteers’ arrangements related to time management. For instance, the operation may contemplate for the activity to be developed, either by using the working time of the employee or their spare time. Similarly, in the case of cash contributions, the operation will guide the way resources donated by volunteers and those provided by the company should be managed.